Getting Pregnant With Diabetes
Controlling blood sugar levels is a major part of diabetic management. Pregnancy and the fertility journey can place additional complications on the process. Lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise can help with weight management and improve fertility.
3 tips for controlling diabetes and improving fertility
Plenty of children are born each year to diabetic parents. When the mother of the child has diabetes, the risks are higher but are still manageable. In addition to staying on top of insulin levels and medications, below are 3 tips for improving fertility with diabetes.
1. Eat smart
Improving diabetes starts with controlling blood sugar levels. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains will help keep blood sugar levels balanced. Elevated blood sugar levels can disrupt ovulation cycles in women and lower sperm count or quality in men. Dietitians can help customize meal plans for individuals struggling to keep blood sugar levels in check.
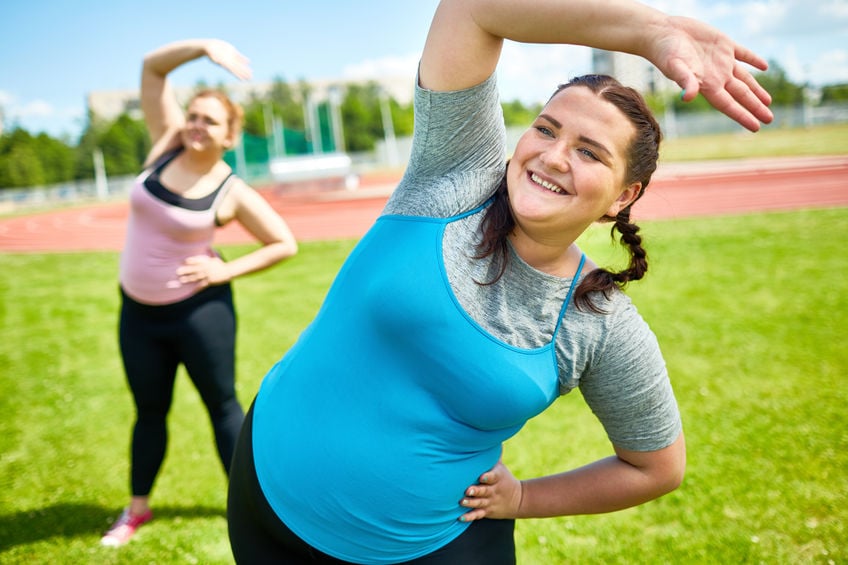
2. Stay active
Maintaining a healthy weight is a large part of diabetic management. Physical activity of 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week can help weight down and improve blood circulation. Physical activity affects blood sugar levels, so additional monitoring before and after exercise will be needed. Obesity can lead to hormonal imbalance and fertility struggles.
3. Manage stress
Cortisol produces excess glucose. High cortisol can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and interfere with blood sugar management. Elevated cortisol can also cause hormonal disruptions for both men and women. Finding ways to de-stress will keep cortisol levels low, increasing the chances of pregnancy.
Why is controlling diabetes important?
Diabetes is entirely manageable, especially if caught early. Medications and lifestyle factors play a major role in the diabetic effect on the body. If blood glucose levels fall too low or go too high, the results can completely disrupt everyday life. Diabetes increases the risk of having a stroke, glaucoma, high blood pressure, kidney failure, nerve damage, and foot problems.
How does diabetes affect pregnancy?
Women with diabetes before pregnancy will need to be watched closely. Pregnancy will affect blood sugar levels, and medication will most likely need to be adjusted. High blood glucose within the first trimester can cause birth defects. Children born to diabetic mothers often have a much higher birth weight due to the excess sugar passed through the placenta and are often delivered via cesarean. The risk of a blood sugar crash right after birth is high, and many of the babies are monitored for several hours after birth. The child of a diabetic mother is also more likely to develop type 1 or type 2 diabetes later in life. Women may also develop diabetes during pregnancy, known as gestational diabetes. Preeclampsia is a risk to all diabetic mothers.
How does diabetes affect fertility?
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to infertility problems among women and men. The leading causes of diabetic-related infertility in women can be attributed to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), irregular menstruation, and premature menopause. For men, the leading causes are erectile dysfunction, low sperm count or poor sperm quality, and low testosterone.
Fertility and diabetes
Diabetes can pose extra complications on fertility, but the symptoms are manageable. Changes in diet, daily exercise, and managing stress can help increase the chances of a pregnancy. Speak with a fertility specialist to learn more about the connection between fertility and diabetes.